12. Create a custom application¶
12.1. Creating a Bluetooth low energy project¶
The recommended way to begin a new Bluetooth low energy project is to use one of the existing examples as a basis. The ble_central and ble_peripheral projects are great starting points for Bluetooth low energy central and peripheral applications respectively, while ble_multi_link is appropriate for applications that need to use both roles simultaneously.
The next sections summarize the different aspects to be considered when using one of these existing projects as a template upon which to build a new application.
12.2. Configuring your application¶
The user can configure any project using a series of MACRO definitions. Some of the options that can be modified are:
- System clocks
- Minimum sleep time
- Charging functionality
- Total heap size
- Chip revision and stepping
- Power up/down peripherals
- Watchdog
- RAM Retention Configuration (refer to section 13.3 of [Ref_04]).
The key file for any project is config/custom_config_qspi.h which
contains all the new configuration options for this project that
overrides the default values in the SDK.
12.3. Adding Bluetooth low energy functionality¶
To extend a Bluetooth low energy project’s functionality, the developer
should become familiar with the Dialog BLE API. These API header files
come with additional Doxygen documentation and are summarized in Table 10. The Doxygen documentation is available in SmartSnippets™
Studio via the API Documentation Open button (at the bottom left) or
directly in the SmartSnippets™ DA1468x SDK via
doc/html/index.html
12.3.1. Including BLE header files¶
| File name | Description |
|---|---|
| sdk/ble/include/ble_att.h | Attribute Protocol API: Mostly definitions. |
| sdk/ble/include/ble_common.h | Common API: Functions used for operations not specific to a certain BLE host software component |
| sdk/ible/include/ble_gap.h | GAP API:
|
| sdk/ble/include/ble_gattc.h | GATT client API:
|
| sdk/ble/include/ble_gatts.h | GATT server API:
|
| sdk/ble/include/ble_storage.h | BLE persistent storage API. |
| sdk/ble/include/ble_uuid.h | BLE UUID declarations and helper functions. |
12.3.2. Adding BLE services¶
Table 11 summarizes the API header files of the Bluetooth low energy
adopted GATT services already implemented by the
SmartSnippets™ DA1468x SDK. These files can be found under
<sdk_root_directory>\sdk\ble_services\include. The developer can use
these APIs to add these services to another project.
| File name | Description |
|---|---|
| ble_service.h | BLE service framework API:
|
| bas.h | Battery Service – BAS |
| bcs.h | Body Composition Service – BCS |
| bms.h | Bond Management Service – BMS |
| cts.h | Current Time Service – CTS |
| dis.h | Device Information Service – DIS |
| dlg_debug.h | Dialog Debug Service |
| dlg_suota.h | Dialog SUOTA Service |
| hids.h | Human Interface Device Service – HID |
| hrs.h | Heart Rate Service – HRS |
| ias.h | Immediate Alert Service – IAS |
| lls.h | Link Loss Service – LLS |
| scps.h | Scan Parameters Service – ScPS |
| sps.h | Serial Port Service – SPS |
| tps.h | Tx Power Service – TPS |
| uds.h | User Data Service – UDS |
| wss.h | Weight Scale Service – WSS |
12.3.3. Bonding information management¶
Most aspects of security are handled seamlessly by the BLE Framework. An application that needs to set-up security, for example initiate pairing, do a security request or set-up encryption using previously exchanged keys, needs only to use the appropriate API. Most details of the procedures are handled internally by the BLE Framework and the application is notified only if intervention is needed or when the procedure is completed.
The generation and storage of the security keys and other bonding information is also handled by the BLE Framework. Persistent storage can also be used to store the security keys and bonding data information in the flash. This allows the information to be retrieved by the BLE Framework after a power cycle and so used to reestablish connections with previously bonded devices.
See also
For more a detailed description about the Bonding management (API’s, Events, MSC’s…) please refer to section 7.3 of [Ref_04].
12.3.4. Hooks¶
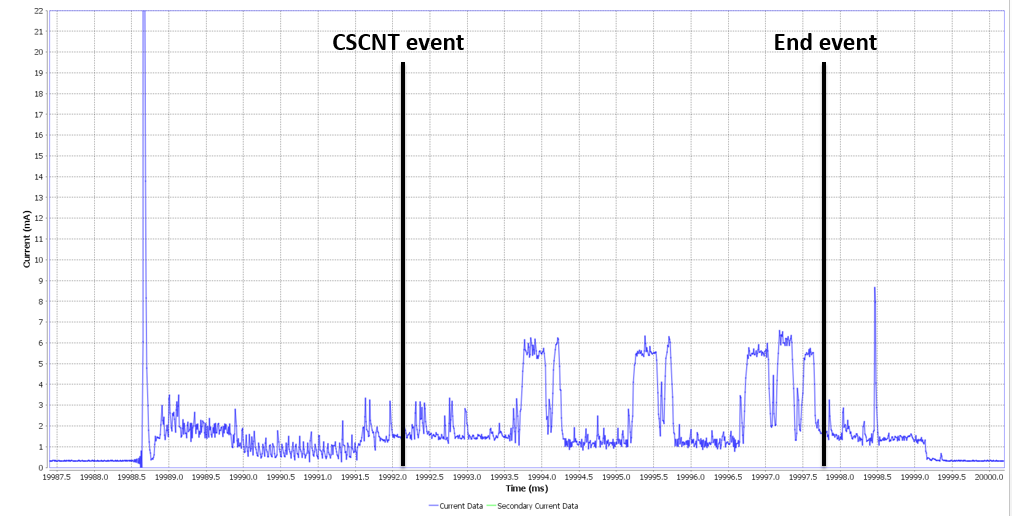
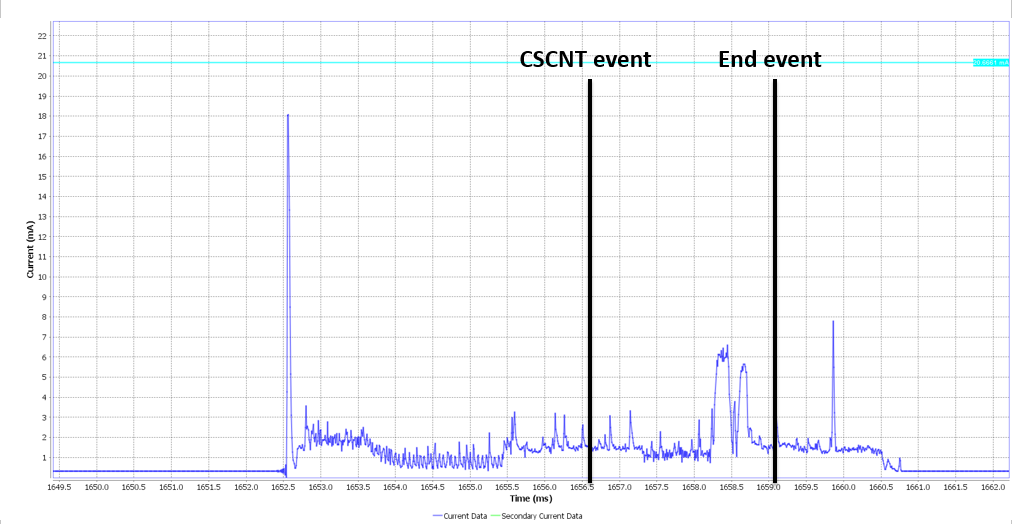
The BLE Hooks mechanism provides the user application a way to be notified about the exact time of occurrence of specific BLE events.
This mechanism enables the user application to receive notifications of BLE Interrupt Service Routine (ISR) events. These events can be received either directly from inside the BLE ISR, or as task notifications to the application task registered to the BLE manager
To enable this feature, define dg_configBLE_EVENT_NOTIF_TYPE to either
BLE_EVENT_NOTIF_USER_ISR or BLE_EVENT_NOTIF_USER_TASK.
When dg_configBLE_EVENT_NOTIF_TYPE == BLE_EVENT_NOTIF_USER_ISR, then the
following macros can be defined in the application code:
| Macro name | Description |
|---|---|
| dg_configBLE_EVENT_NOTIF_HOOK_END_EVENT | The BLE End Event |
| dg_configBLE_EVENT_NOTIF_HOOK_CSCNT_EVENT | The BLE CSCNT Event |
| dg_configBLE_EVENT_NOTIF_HOOK_FINE_EVENT | The BLE FINE Event |
These macros must be set to the names of functions defined inside the user application and which have the following prototype:
void func(void);
Note
The user application does not need to explicitly define the prototype.
If a macro is not defined, then the respective notification is suppressed.
Warning
These functions are called in an ISR context, directly from the BLE ISR. They should therefore be very fast and should NEVER block.
When dg_configBLE_EVENT_NOTIF_TYPE == BLE_EVENT_NOTIF_USER_TASK, the
user application receives task notifications on the task registered to
the BLE manager. Notifications are received using the following bit
masks:
| Macro name | Description |
|---|---|
| dg_configBLE_EVENT_NOTIF_MASK_END _EVENT | End Event Mask (Default: bit 24) |
| dg_configBLE_EVENT_NOTIF_MASK_CSC NT_EVENT | CSCNT Event Mask (Default: bit 25) |
| dg_configBLE_EVENT_NOTIF_MASK_FIN E_EVENT | FINE Event Mask (Default: bit 26) |
The bit mask for each of the macros in Table 13 can be redefined as needed.
If one of the macros for callback functions listed in Table 12 (for direct ISR notifications) is defined then the ISR mode takes precedence and the function with the same name is called directly from the ISR instead of sending a task notification for this particular event to the application task.
The macro dg_configBLE_EVENT_NOTIF_RUNTIME_CONTROL (Default: 1)
enables/disables runtime control/masking of notifications.
If dg_configBLE_EVENT_NOTIF_RUNTIME_CONTROL == 1 then task notifications
must be enabled/disabled using the
ble_event_notif[enable|disable]_[end|cscnt|fine]_event() functions. By
default, all notifications are disabled.
If dg_configBLE_EVENT_NOTIF_RUNTIME_CONTROL == 0, all notifications are
sent unconditionally to the application task.